What are hash values in Git?
Git uses the SHA-1 hash algorithm to generate a number for each change in a document. The numbers are often referred to as SHA values.
Checksum algorithms convert data into a simple number called a checksum. The same data always results in the same checksum in order to guarantee data integrity.
Git generates a 40-character hexadecimal string for each commit. Example:
7a7a472abf3dd9643fd615f6da379c4acb3e3a
Git creates these values based on what's in the data itself. This means you can't change the commit message, commit author, or the "parent" of the commit without also changing the SHA value.
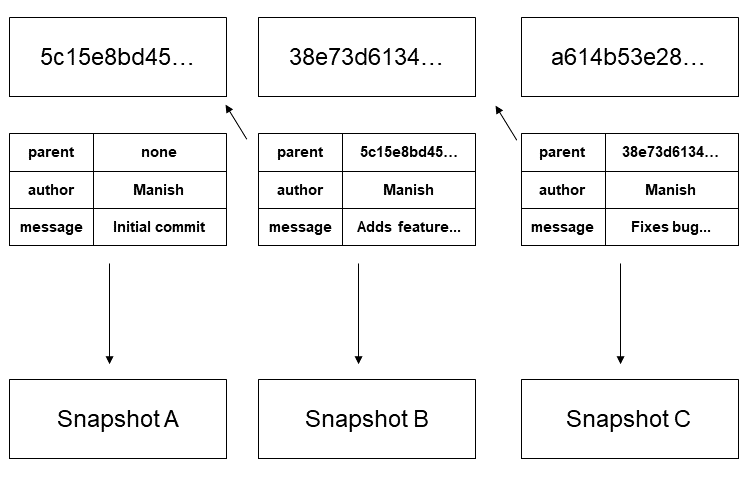
When Git generates snapshot A, it takes the parent, the author, the message, and all of the code changes, and generates its SHA value.
Then, when Git makes snapshot B, it goes through that same process. However, it includes the SHA value from snapshot A, so that it's linked to A.
If we were to change something in snapshot A, then A's SHA value would change and B wouldn't point to it anymore.
Sources
- Skoglund, K. (2019). Git Essential Training: The Basics [Video]. LinkedIn Learning. https://www.linkedin.com/learning/git-essential-training-the-basics
- Pro Git