What are HTTP messages?
HTTP messages are how data is exchanged between a server and a client.
There are two types of HTTP messages:
-
HTTP requests, sent by the client to trigger an action on the server.
-
HTTP responses, the answer from the server.
Clients and servers communicate by exchanging individual messages (as opposed to a stream of data). The messages are human-readable.
Structure of requests and responses
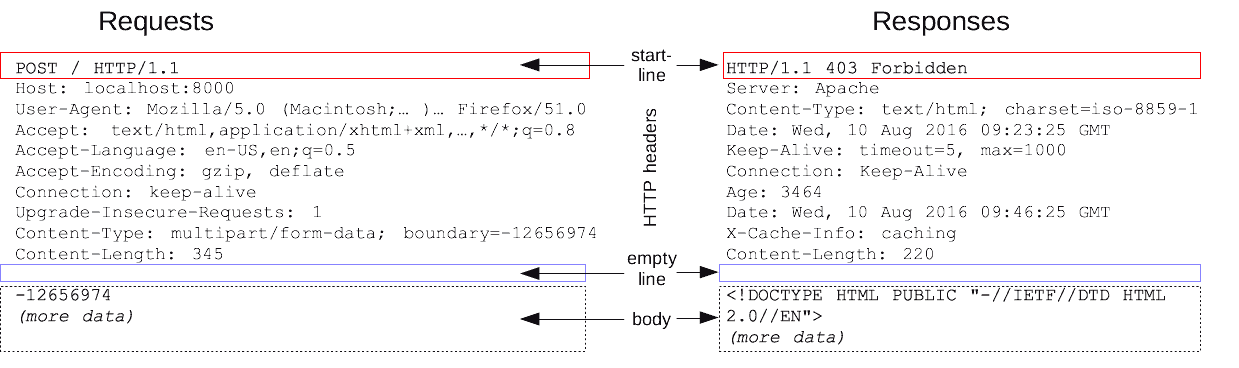
HTTP requests and responses share a similar structure and include:
-
a start-line that describes the request being made, or its success status. Always a single line.
-
optional HTTP headers for specifying the request or describing the body included in the message.
Header fields are key-value pairs separated by colons.
-
a blank line indicating all meta-information for the request has been sent.
-
an optional body that contains data associated with the request or the document associated with the response.
HTTP Request
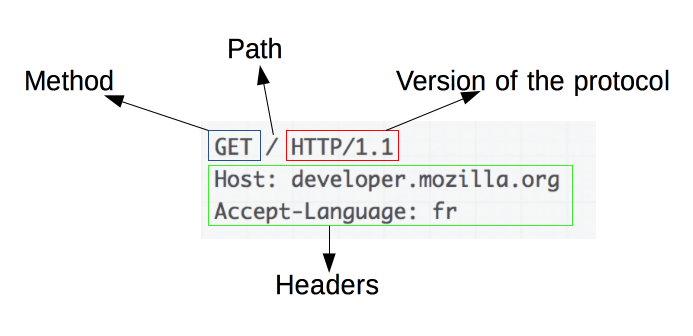
HTTP Method
Defines the operation the client wants to perform. Options include:
GETPOSTPUTDELETE
Path
The path of the requested resource.
Version
Version of HTTP protocol
Headers
Optional headers to convey additional information for the servers
Body
A POST method would contain the resource being sent to the server.
HTTP Response
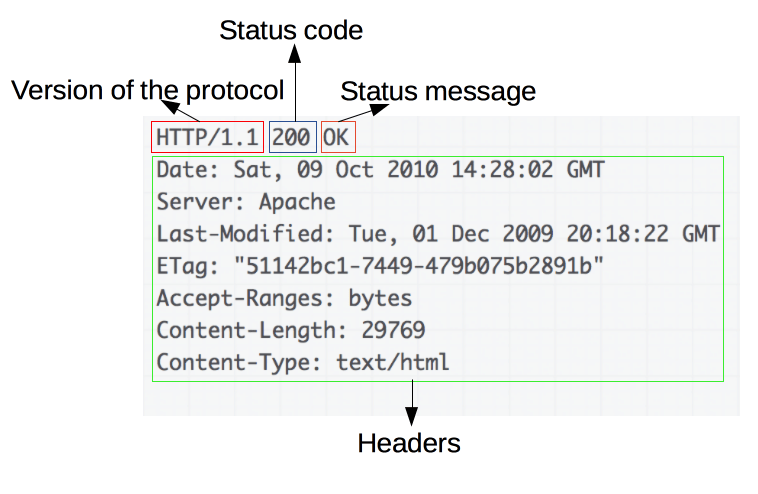
Version
Version of HTTP protocol
Status code
Indicates whether a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed.
Status message
A non-authoritative short description of the status code.
Headers
HTTP headers, like those for requests.
Header fields are key-value pairs separated by colons.
Body
Optional. Contains the fetched resource.