What are HTTP requests?
HTTP requests are messages sent by the client to initiate an action on the server.
Start-line
The start-line of HTTP requests contains three elements:
1. HTTP method
HTTP verbs indicate the action to be performed. These actions include:
GET: fetch a resourcePOST: push data to the server to create a new resourceDELETE: delete a resource from the serverPUT: update a resource on the server
2. Request target
Target is usually a URL. Options include:
- Absolute path followed by a
?and query string.- This is the most common form and is used with HTTP methods.
- Complete URL (absolute form)
- Mostly used with
GETwhen connected to a proxy.
- Mostly used with
- Authority component of URL
- Consists of the domain name and the port (optional).
- Asterisk form
- A simple asterisk (
*) used withOPTIONS, representing the server as a whole.
- A simple asterisk (
3. HTTP version
Defines the structure of the remaining message, acting as an indicator of the expected version to use for the response.
Headers
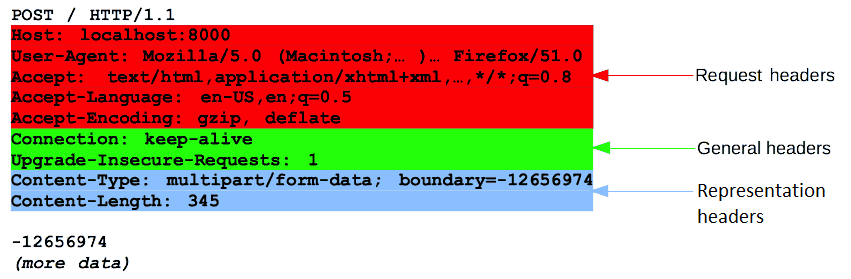
HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response.
A request header is a type of HTTP header that can be used in a request to provide information about the request context, so that the server can tailor the response.
Headers are in key-value pairs separated by a colon.
A representation header is a type of HTTP header that describes the particular representation of the resource sent in an HTTP message body.
Example:
Content-Length: 100
Body
The body is the final part of an HTTP request. Not all requests need one, such as GET, HEAD, DELETE, or OPTIONS.